What Your Child Will Learn in High School American Government
Essential Curriculum For American Government
Foundations of Government
Goal 1: Students will understand the purposes of government and governmental systems.
Objectives:
- Define government and explain its importance.
- List the purposes of government.
- Describe the structure of the Preamble.
Goal 2: Students will analyze advantages and disadvantages of various types of governments throughout the world.
Objectives:
- Describe the differences, advantages, and disadvantages among types of governments, from authoritarian to democratic.
- Identify the features of unitary, federal, and confederate systems of government.
Goal 3: Students will understand the historical foundations of American government.
Objectives:
- Identify how philosophers have described the nature and purpose of the state and analyze the origins and historical development of values and principles, that have influenced and shaped the United States constitutional system.
- Explain the importance, ideals, and contributions of common law and key historical documents leading to the Declaration of Independence.
- Relate the colonial experience to the overall development and design of the American governmental system through the development of the Articles of Confederation, the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, and relevant Amendments.
Goal 4: Students will understand key principles implemented in American Government.
Objectives:
- Analyze the meaning and importance of values and principles fundamental to democracy in the United States.
- Apply the basic principles on which the United States Constitution is based to contemporary situations.
- Explain how the Constitution ensures the people’s authority over the government.
Goal 5: Students will evaluate the structure and content of the United States Constitution.
Objectives:
- Analyze the structure of the Constitution as a “living document.”
- Explain the freedoms guaranteed by the Bill of Rights and corresponding responsibilities of citizens.
Goal 6: Students will evaluate the federalism of the United States and analyze how it assists and impedes the function of government.
Objectives:
- Explain how the United States Constitution grants and distributes powers to national and state governments (federalism) including reserved, delegated, concurrent, and denied powers.
- Analyze issues related to the division of powers and its impact on institutions, groups, and individuals (e.g. taxation, welfare, regulation, education).
Political Structures
Goal 1: Students will understand the structures and functions of the legislative branches on the national, state and local levels.
Objectives:
- Explain how the legislative bodies at the different levels differ in structure, membership, and responsibilities.
- Describe the special powers granted to legislative bodies.
- Analyze the powers, responsibilities and limitations of legislative bodies in relation to the other two branches.
- Describe how legislation is enacted at national, state, and local levels.
- Analyze the structure of elections for the legislative branch.
Goal 2: Students will understand the structures and functions of the executive branches at the national, state and local levels.
Objectives:
- Describe the qualifications, duties, and powers of the president.
- Describe the qualifications, duties, and powers of the governor.
- Describe the qualifications, duties, and powers of the county executive
- Describe the qualifications, duties, and powers of a mayor.
- Analyze how the other branches balance the powers of the executive branch.
- Identify the importance of the executive departments, agencies, and independent regulatory agencies at the national, state, and local levels.
- Compare and contrast an executive order with a law.
- Analyze the structure of elections for the executive branch.
Goal 3: Students will understand the role of political parties in the political structures of government on the national, state, and local levels.
Objectives:
- Analyze the roles of political parties, campaigns and elections in United States politics.
- Determine how the public agenda is set and shaped by political parties.
- Explain the functions, impact, and ideology of American political parties and their role in elections and government.
Law and Policy
Goal 1: Students will understand the structures and functions of the judicial branch at the national and state levels.
Objectives:
- Identify the structure and function of the court system at each level of government.
- Describe the membership and function of the United States Supreme Court.
- Describe the process for judicial appointment.
- Explain how the Supreme Court operates including the process.
- Identify the roles of the Maryland courts and describe their authority.
- Identify limitations placed on judicial branches.
- Compare the differences between substantive and procedural due process.
Goal 2: Students will analyze the impact of landmark Supreme Court decisions on governmental powers, rights, and responsibilities of citizens in our changing society.
Objectives:
- Explain the significance of landmark Supreme Court decisions in relation to due process and civil rights.
- Explain how the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights guarantee civil liberties for American citizens.
- Explain how the laws of Howard County forbid discriminatory practices based upon race, religion, creed, disability, color, gender, national origin, occupation, marital status, political opinion, sexual orientation, personal appearance, familial status, or sources of income.
Goal 3: Students will analyze elements, proceedings, and decisions related to criminal law.
Objectives:
- Categorize types of crimes.
- Evaluate the balance between the protection of civil rights in a free society and the need to protect society from criminal behavior.
- Interpret the freedoms guaranteed by the Bill of Rights and amendments as they pertain to judicial proceedings.
- Summarize the proceedings, which occur before, during, and after a criminal trial.
Goal 4: Students will analyze elements, proceedings, and decisions related to civil law.
Objectives:
- Explain the process of civil law cases.
- Distinguish between the varieties of civil law, including contract, tort, property, and family.
Goal 5: Students will understand the role of government in shaping domestic public policy.
Objectives:
- Explain how government at the national, state, and local levels develops public policy affecting health, environmental, land use, economic, political, social equity (including gender discrimination, affirmative action, and Native American rights,) internal security, and education matters.
- Explain the role of the federal government in setting immigration and naturalization policies.
- Describe how regional interests impact political decisions and government policy.
- Examine how regional interests in the state of Maryland have impacted decision making and government policy of the state General Assembly.
Goal 6: Students will understand the roles played by individuals, groups, and institutions in influencing governmental policies and actions.
Objectives:
- Analyze the role of public opinion in American politics.
- Determine how the public agenda is set and shaped by the media.
- Evaluate the role of lobbyists and private and public interest groups in influencing governmental policy.
- Determine how the public agenda is set and shaped by interest groups and lobbyists.
- Determine how the public agenda is set and shaped by individual citizens.
- Explain how the individual can play a role in influencing governmental policy.
Goal 7: Students will understand the role of the federal government in shaping foreign policy.
Objectives:
- Explain how nation-states interact with each other through trade, diplomacy, treaties, international law, and military alliances.
- Describe the various means used by the United States in developing and carrying out foreign policy including diplomacy; ideology; economic, military, and humanitarian aid; military intervention; and sanctions.
- Evaluate significant issues of United States foreign policy in light of national interests, values, and principles.
- Research the ways in which the United States can further its foreign policy interest through economic practices including foreign and humanitarian aid.
Economics and Financial Literacy
Goal 1: Students will understand basic economic concepts and systems.
Objectives:
- Analyze the economic concepts of wants, needs, and scarcity.
- Identify the factors of production: labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
- Define opportunity cost.
- Explain the relationship between supply, demand, and price.
- Summarize how traditional, command, and market economies answer the basic economic questions of what to produce, how to produce, how much to produce, and how to distribute goods and services.
Goal 2: Students will understand the forces that direct the United States market system and the role of the government in establishing a domestic economic policy.
Objectives:
- Construct the phases of the business cycle. Describe the characteristics and use of fiscal policy including taxation and spending.
- Describe the characteristics and use of monetary policy and the role of the Federal Reserve.
- Support ways in which the government provides for the economic welfare of the people including public assistance, Social Security, and minimum wage.
- Identify ways in which the government seeks to achieve socioeconomic goals.
- Select issues surrounding conflicting contemporary economic public policy goals.
Goal 3: Students will understand the role of the government in establishing economic policies in the global arena.
Objectives:
- Determine the impact of multinational corporations on international trade.
- Interpret the economic interdependence among the United States and other nations.
- Compare the American labor force with that of other nations.
- Examine the economic exploitation of foreign workers in relation to trade issues.
Goal 4: Students will understand the issues associated with personal economic decision making.
Objectives:
- Explain what money is and describe how it is used in our society.
- Explain how one’s financial goals are directly related to one’s personal investment in education and decision making in life choices.
- Identify sources of income and personal wages.
- Explain the differences between gross and net pay.
- Read a pay stub and identify the types of deductions taken from wages.
- Fill out a simple tax form.
- Compare the differences between various savings and checking options.
- Fill out a check and balance on a checkbook.
- Identify the types of loans offered by financial institutions.
- Explain the financial obligations, consequences, and costs of borrowing money.
- Describe how to manage credit responsibly.
- Demonstrate how to create a responsible personal budget based on personal income.
- Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of using credit.
- Compare the types of insurance options provided for consumers.
- Compare the characteristics and risks of different types of personal investments.
- Discover practices used by wise consumers.
- Determine the role of advertising in influencing consumer behavior.
- Describe the financing options for continuing or higher education.
- Categorize taxes as progressive, regressive, and proportional.
- Distinguish between taxes designed to raise revenue and those designed to influence behavior.
Sample Test Questions
What is the opportunity cost for state governments that spend state money during natural disasters?
- Main highways between states may be blocked.
- Prices for snow removal equipment may increase.
- Other services offered by the states may have to be cut.
- State governments may receive additional highway funds.
In which of these cases did the U.S. Supreme Court interpret the “necessary and proper” clause of the United States Constitution?
- Marbury vs. Madison
- McCulloch vs. Maryland
- Tinker vs. Des Moines School District
- Brown vs. Board of Education of Topeka
Read the excerpt below.
“After [dividing] the several classes of power, as they may in their nature be legislative, executive, or judiciary, the next and most difficult task is to provide some practical security for each, against the invasion of the others.”
—The Federalist, No. 48
Which of these principles of government is described in the excerpt?
- due process.
- popular sovereignty.
- checks and balances.
- representative democracy.
In 1974, Congress passed a law that restricts financial institutions from considering factors such as race, religion, gender, or age when considering an applicant for credit.
This law was most likely passed to:
- reduce the number of businesses offering financial loans.
- protect groups of people from unfair business practices.
- increase the length of time it takes to process credit applications.
- prohibit businesses from verifying financial information.
Which of these best explains why local governments create zoning laws?
- to require builders to pursue creative designs.
- to increase the number of jobs in a community.
- to encourage businesses and citizens to recycle more goods.
- to control the use of buildings and land within a community.
Study the political cartoon below.

What would be the role of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the situation shown in the cartoon?
- setting prices for the sale of electricity across the United States
- preventing companies from developing their own clean air policy
- deciding how much energy the United States should produce
- ensuring that companies follow pollution control laws
Read the graph below.
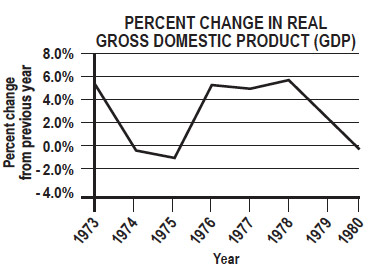
Which of these best characterizes the condition of the United States’ economy between 1975 and 1978?
- a rapidly rising unemployment rate
- increased economic growth
- a constant inflation rate
- steady interest rates